- Mail:
- info@digital4pro.com
From Artificial Intelligence to Deep Learning

Dall’Intelligenza Artificiale al Deep Learning
10 Novembre 2020
Management by Exception
11 Novembre 2020In computer science, algorithm means a series of well-defined instructions given to a machine to perform certain actions that allow to solve a certain problem. Normally, the algorithm is designed and developed to solve a specific problem and does not change over time.
Artificial Intelligence
In an AI system, however, the algorithm learns and modifies itself based on the data it receives. The more data is analyzed by the AI, the better the final result will be. So in an AI system the machine is subjected to the results it has to obtain and it will be the machine itself, through a training path, to find the best way to achieve that result.
Artificial Intelligence is a set of technologies that includes Machine Learning. In turn, machine learning includes Artificial Neural Networks (Artificial Neural Networks). A subset of Artificial Neural Networks are Deep Learning networks.
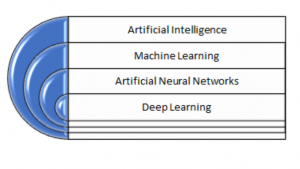
Figure 1 – From Artificial Intelligence to Deep Learning
Example of Artificial Intelligence:
- AlphaGo, developed by Google DeepMind between 2014 and 2015, has become the first program capable of defeating a professional human player at Go, an ancient Chinese strategy game. AlphaGo has learned the rules of the game by analyzing and interpreting strategies from several thousand games.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that deals with creating systems that learn from the data they use. In Machine Learning the information or, better, the models are acquired directly from the data, without the use of predetermined equations.
In a problem solved in the traditional way it is the programmer who describes in detail the various steps necessary for the solution.
With Machine Learning, through appropriate mathematical algorithms exposed to a given set of data in a defined initial phase of training (or learning) and passing through a second phase of testing (or evaluation of results) for the optimization of the parameters, the function capable of identifying within a different set of data the most likely solution is obtained independently, possibly indicating a degree of confidence in the estimate. In practice, the system obtains the function itself. This system, composed of trained algorithm, data and parameters, is called a model.
The automatic learning is to the base of the systems of artificial intelligence in how much it enables the machines to learn without being explicitly and preventively programmed.
Machine Learning models are very effective in identifying correlations in huge data sets, taking into account a number of variables that would be unthinkable for a human being.
Machine Learning has two important advantages over other techniques:
- Tolerance to “dirty” data such as duplicate records, incorrectly analyzed fields or incomplete, incorrect or obsolete information;
- Flexibility in machine learning. As the data provided to the algorithm grows, so does the ability to learn and improve the quality of the algorithm.
Examples of Machine Learning:
- Marketing analysis tools based on machine learning can allow you to evaluate existing data and make reliable predictions about what type of post can generate conversions, what content customers want to read and what marketing channels lead to the purchase;
- Chatbot can be based on machine learning. By focusing on the keywords contained in the user’s request, they can guide the customer to the desired information through various questions;
- Netflix and Amazon machine learning enables systems to successfully predict which products and services customers will potentially be interested in. These systems are able to provide very detailed suggestions to encourage the sale of products and highly customizable items.
Artificial Neural Networks
The Artificial Neural Network consists of a mathematical model of calculation that simulates the behavior of biological neural networks of the human brain. The latter, unlike machines, is able to perform several independent operations at the same time and is therefore a model to aspire to.
An Artificial Neural Network can be formed both by software programs and hardware and is based on a network of interconnections between three types of nodes that exchange information:
- I – input (input nodes): the nodes that receive and process signals coming from outside adapting them to internal nodes;
- H – hidden (intermediate nodes): the nodes that realize the real elaboration process each one independently from the other. The intermediate nodes are called network layers (or layers);
- O – output (output nodes): the nodes that collect the results of the processing of the H layer and transmit them to the output.
Examples of Artificial Neural Network are for example:
- Natural language processing capable of understanding word and text in near real time, for the creation of advanced virtual assistants. Unlike Machine Learning based assistants, Deep Learning based chatbots include natural human language and are not based on the use of specific keywords;
- Machine vision systems for image recognition and classification;
- Search optimization and information retrieval;
- Voice Assistants, through which users can ask, through voice, to place orders, send e-mails, create reports or perform searches (such as Siri, Alexa and Google Home).
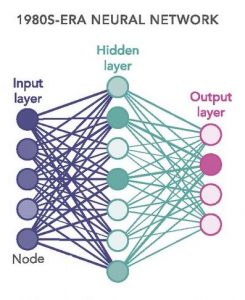
Figure 2 – Model of an artificial neural network.
Deep Learning
A neural network consisting of two or more series of intermediate nodes allows a very powerful form of processing, called deep learning.
Deep Learning is the ability of an algorithm to learn from input data through successive layers of processing.
Deep learning uses multiple levels of filters to know the significant characteristics of the data.
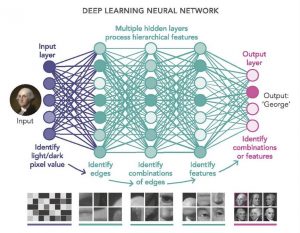
Figure 3 – Deep Learning Model
Example of Deep Learning:
- Machines capable of recognizing a person through the tone of his voice or the physiognomy of his face.
Bibliography:
- Deep Learning, Ian Goodfellow
- Deep Learning, John D. Kelleher




